Hi ![]()
I am new to acados and I am facing some issues setting up an external cost function for a NMPC problem through python interface. The optimal control problem at hand is the classic cartpole inverted pendulum problem, which I was able to successfully set up on do-mpc and using casadi. However, both of these packages do not solve the NLP problem fast enough (with the compute I have) for real-time implementation (>=40 Hz needed). Hence, I turned to acados and I am impressed by the computational efficiency!
To make the controller solve the pendulum problem regardless of the angle of the pole (and to set it up for double pendulum in the future), I would like to set up the cost function to minimize the kinetic energy, maximize the potential energy, with setpoint tracking on the x position, and move suppression:
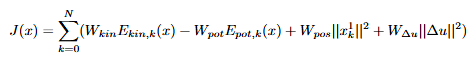
System Model
Code
def pendulum_ode_model(m_cart, mp1, l1, g=9.81, b_c=0.0, b_p=0.05) -> AcadosModel:
model_name = 'pendulum'
# constants
m_cart = m_cart # mass of the cart [kg]
m = mp1 # mass of the ball [kg]
g = g # gravity constant [m/s^2]
l = l1 # length of the rod [m]
b_c = b_c # friction coefficient for the cart
b_p = b_p # friction coefficient for the pendulum
# set up states & controls
x1 = SX.sym('x1')
theta = SX.sym('theta')
v1 = SX.sym('v1')
dtheta = SX.sym('dtheta')
u_prev = SX.sym('u_prev')
x = vertcat(x1, theta, v1, dtheta, u_prev)
F = SX.sym('F')
u = vertcat(F)
# xdot
x1_dot = SX.sym('x1_dot')
theta_dot = SX.sym('theta_dot')
v1_dot = SX.sym('v1_dot')
dtheta_dot = SX.sym('dtheta_dot')
u_prev_dot = SX.sym('u_prev_dot')
xdot = vertcat(x1_dot, theta_dot, v1_dot, dtheta_dot, u_prev_dot)
# dynamics
cos_theta = cos(theta)
sin_theta = sin(theta)
denominator = m_cart + m - m*cos_theta*cos_theta
f_expl = vertcat(v1,
dtheta,
(-m*l*sin_theta*dtheta*dtheta + m*g*cos_theta*sin_theta + F - b_c*v1)/denominator,
(-m*l*cos_theta*sin_theta*dtheta*dtheta + F*cos_theta + (m_cart+m)*g*sin_theta - b_p*dtheta)/(l*denominator),
F
)
f_impl = xdot - f_expl
model = AcadosModel()
model.f_impl_expr = f_impl
model.f_expl_expr = f_expl
model.x = x
model.xdot = xdot
model.u = u
# model.z = u_prev
model.name = model_name
# add potential and kinetic energy expressions
E_kin_cart = 1 / 2 * m_cart * v1**2
E_kin_pendulum = 1 / 2 * m * ((v1 + l * dtheta * cos(theta))**2 + (l * dtheta * sin(theta))**2) + 1 / 2 * (m * l**2 / 3) * dtheta**2
E_kin = E_kin_cart + E_kin_pendulum
E_pot = m * g * l * cos(theta)
model.E_kin = E_kin
model.E_pot = E_pot
# store meta information
model.x_labels = ['$x$ [m]', r'$\theta$ [rad]', '$v$ [m]', r'$\dot{\theta}$ [rad/s]', '$u_{prev}$ [N]']
model.u_labels = ['$F$']
model.t_label = '$t$ [s]'
return model
Following the example in the acados repo, I was able to formulate the NMPC with a NONLINEAR_LS cost function, as can be seen in this code:
Code
def formulate_pendulum_sim(model: AcadosModel,
dt: float = 0.05) -> AcadosSimSolver:
"""
Construct the simulator/integrator for the plant model.
"""
model.name += '_plant_sim'
sim = AcadosSim()
sim.model = model
sim.solver_options.T = dt
sim.solver_options.integrator_type = 'IRK'
sim.solver_options.num_stages = 4
sim.solver_options.num_steps = 3
sim.solver_options.newton_iter = 3
sim.solver_options.collocation_type = 'GAUSS_LEGENDRE'
sim_solver = AcadosSimSolver(sim)
return sim_solver
def formulate_pendulum_mpc(model: AcadosModel, N: int = 20, Tf: float = 1.0, RTI: bool = False,
Q: np.ndarray = np.diag([1e3, 1e3, 1e-2, 1e-2]),
Q_e: np.ndarray = np.diag([1e3, 1e3, 1e-2, 1e-2]),
cost_type: str = 'NONLINEAR_LS',
use_energy: bool = True,
x0: np.ndarray = np.array([0.0, np.pi, 0.0, 0.0]),
u_min: np.ndarray = np.array([-10.0]),
u_max: np.ndarray = np.array([10.0]),
x_min: np.ndarray = np.array([-0.7, -np.inf, -np.inf, -np.inf]),
x_max: np.ndarray = np.array([0.7, np.inf, np.inf, np.inf])
) -> AcadosOcp:
"""
Formulate the MPC problem for the pendulum model.
"""
ocp = AcadosOcp()
ocp.model = model
ocp.solver_options.N_horizon = N
ocp.solver_options.tf = Tf
nx = model.x.rows()
nu = model.u.rows()
ny = nx + nu
ny_e = nx
x = ocp.model.x
u = ocp.model.u
E_kin = ocp.model.E_kin
E_pot = ocp.model.E_pot
u_prev = x[-1]
if cost_type == 'NONLINEAR_LS':
# Nonlinear least squares cost using kinetic and potential energy, cart position, and move suppression
ocp.cost.cost_type = cost_type
ocp.cost.cost_type_e = cost_type
ocp.solver_options.hessian_approx = 'GAUSS_NEWTON'
if use_energy:
ocp.model.cost_y_expr = ca.vertcat(E_kin, -E_pot, x[0], (u - u_prev))
ocp.model.cost_y_expr_e = ca.vertcat(E_kin, -E_pot, x[0], 0.0)
n_ref = ocp.model.cost_y_expr.rows()
ocp.cost.cost_type = cost_type
ocp.cost.W = Q
ocp.cost.W_e = Q_e
ocp.cost.yref = np.zeros((n_ref,))
ocp.cost.yref_e = np.zeros((n_ref,))
else:
ocp.model.cost_y_expr = ca.vertcat(x[:-1], u - u_prev)
ocp.model.cost_y_expr_e = x[:-1]
ocp.cost.W = Q
ocp.cost.W_e = Q_e
n_ref = ocp.model.cost_y_expr.rows()
n_ref_e = ocp.model.cost_y_expr_e.rows()
ocp.cost.yref = np.zeros((n_ref,))
ocp.cost.yref_e = np.zeros((n_ref_e,))
elif cost_type == 'EXTERNAL':
# External cost function
ocp.cost.cost_type = cost_type
ocp.cost.cost_type_e = cost_type
# Set up the external cost function
ocp.model.cost_expr_ext_cost = Q[0,0] * E_kin + Q[1,1] * (-E_pot) + Q[2,2] * (ocp.model.x[0]**2) + Q[3,3] * (u - u_prev)**2
ocp.model.cost_expr_ext_cost_e = Q_e[0,0] * E_kin + Q_e[1,1] * (-E_pot) + Q_e[2,2] * ocp.model.x[0]**2
ext_cost_use_num_hess = False # use numerical Hessian for external cost
ocp.solver_options.ext_cost_num_hess = ext_cost_use_num_hess
ocp.solver_options.hessian_approx = 'EXACT'
ocp.solver_options.globalization_alpha_min = 1e-25
# set constraints
ocp.constraints.lbu = u_min
ocp.constraints.ubu = u_max
ocp.constraints.idxbu = np.arange(nu)
ocp.constraints.lbx = x_min
ocp.constraints.ubx = x_max
ocp.constraints.idxbx = np.arange(nx)
ocp.constraints.x0 = x0
ocp.solver_options.qp_solver = 'FULL_CONDENSING_HPIPM'
ocp.solver_options.qp_solver = 'PARTIAL_CONDENSING_HPIPM'
# ocp.solver_options.qp_solver = 'PARTIAL_CONDENSING_OSQP'
# ocp.solver_options.qp_solver = 'FULL_CONDENSING_QPOASES'
ocp.solver_options.integrator_type = 'IRK'
ocp.solver_options.nlp_solver_type = 'SQP' # SQP_RTI
# ocp.solver_options.sim_method_num_steps = 10
ocp.solver_options.sim_method_newton_iter = 5
ocp.solver_options.tol = 1e-12
# ocp.solver_options.tol = 1e-5
# ocp.solver_options.sim_method_newton_tol = 1e-5
ocp.solver_options.qp_solver_cond_N = N
if RTI:
ocp.solver_options.nlp_solver_type = 'SQP_RTI'
else:
ocp.solver_options.nlp_solver_type = 'SQP'
ocp.solver_options.qp_solver_iter_max = 5000
ocp.solver_options.nlp_solver_max_iter = 5000
ocp.solver_options.globalization = 'MERIT_BACKTRACKING'
solver_json = 'acados_ocp_' + model.name + '.json'
acados_ocp_solver = AcadosOcpSolver(ocp, json_file = solver_json)
return acados_ocp_solver
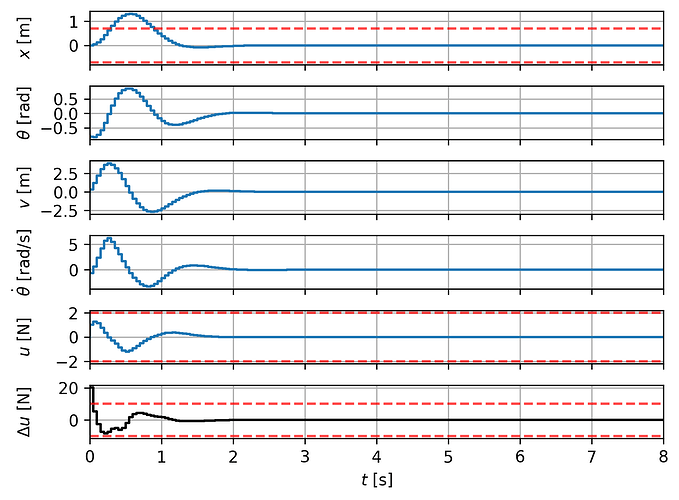
This formulation does not really follow the objective function presented at the top. More importantly, it seems that there are some robustness issues when utilizing this NONLINEAR_LS cost function. I noticed this as running the optimizer with SQP_RTI works well for all initial conditions, but this is not the case using just SQP. I also run into robustness issues when there is a slight plant-model mismatch or measurement noise.
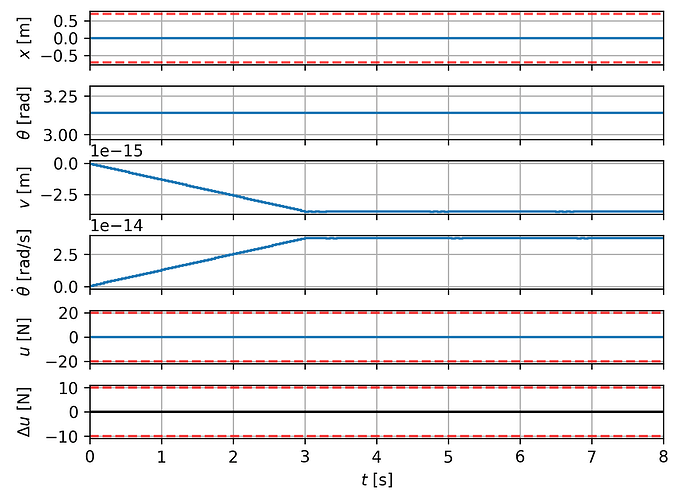
The code above also includes my attempt at setting up an EXTERNAL cost function, which has not been successful thus far. Whenever I run it with the EXTERNAL cost, I end up with the following message:
SQP_RTI: QP solver returned error status 3 QP iteration 15.
The controller does not make any significant moves in the manipulated variable with the EXTERNAL cost function set up. I tried reducing globalization_alpha_min but that does not seem to fix the issue. I also tried using different weights with no luck.
NMPC Setup in main.py
Code
def main():
# Define parameters
m_cart = 0.035 # mass of the cart [kg]
mp1 = 0.034 # mass of the pendulum [kg]
l1 = 0.25 # length of the rod [m]
g = 9.81 # gravity constant [m/s^2]
b_c = 0.0 # friction coefficient for the cart
b_p = 0.0 # friction coefficient for the pendulum
Tsim = 8.0 # final time for simulation [s]
dt = 0.025 # time step for simulation [s] and sampling time for the ocp
Nsim = int(Tsim / dt) # number of steps
Tf = 1.0 # length of the prediction horizon [s]
N_horizon = int(Tf/dt) # MPC number of stages in the prediction horizon
# get the pendulum model
model = pendulum_ode_model(m_cart, mp1, l1, g, b_c, b_p)
nx = model.x.rows() # number of states
nu = model.u.rows() # number of controls
# Initiate simulation integrator
sim_solver = formulate_pendulum_sim(model, dt=dt)
# Formulate the MPC controller as an OCP solver
cost_type = 'EXTERNAL' # cost type
# cost_type = 'EXTERNAL' # cost type for external cost function
RTI = True # Real-Time Iteration
use_energy = True # use energy in the cost function
if cost_type == 'NONLINEAR_LS':
if use_energy:
Q = 200*np.diag([1.0, 30.0, 1.0, 0.6]) # output reference tracking cost matrix
Q_e = 200*np.diag([1.0, 15.0, 0.75, 0]) # terminal output reference tracking cost matrix
else:
Q = 2*np.diag([1e2, 1e2, 0, 0, 4e-1]) # state reference tracking cost matrix
Q_e = 2*np.diag([1e2, 1e2, 0, 0]) # terminal state reference tracking cost matrix
elif cost_type == 'EXTERNAL':
Q = 200*np.diag([1.0, 10.0, 15.0, 0.7]) # weights for the external cost function
Q_e = 200*np.diag([1.0, 1.0, 0.75, 0]) # terminal weights for the external cost function
x0 = np.array([0.0, 1*np.pi, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]) # initial state [x1, theta, v1, dtheta, u_prev]
u_min = np.array([-2.0]) # minimum control input
u_max = np.array([2.0]) # maximum control input
x_min = np.array([-0.5, -ACADOS_INFTY, -ACADOS_INFTY, -ACADOS_INFTY, -ACADOS_INFTY]) # minimum state
x_max = np.array([0.5, ACADOS_INFTY, ACADOS_INFTY, ACADOS_INFTY, ACADOS_INFTY]) # maximum state
controller_config = {
'N': N_horizon, # number of stages in the prediction horizon
'Tf': Tf, # length of the prediction horizon [s]
'Q': Q, # state cost matrix
'Q_e': Q_e, # terminal state cost matrix
'x0': x0, # initial state
'u_min': u_min, # minimum control input
'u_max': u_max, # maximum control input
'x_min': x_min, # minimum state
'x_max': x_max, # maximum state
'cost_type': cost_type, # cost type
'RTI': RTI, # Real-Time Iteration
'use_energy': use_energy, # use energy in the cost function
}
mpc = formulate_pendulum_mpc(model, **controller_config)
Questions
Is there anything I am missing or overlooking in my code, especially for the EXTERNAL cost set up?
Are there any additional examples for EXTERNAL cost set up that can help guide me with this project?
Could the numerical issues cause the lack of robustness in the NONLINEAR_LS cost formulation (the masses of my 3D printed setup in the lab are quite low)? and if so, would adjusting the scaling result in more robust NMPC?
Thank you for your advice! ![]()